Assignments > Activity 6: Intro to SQLAlchemy
As stated on the SQL Alchemy project page: “SQLAlchemy is the Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper that gives application developers the full power and flexibility of SQL.” In other words, SQL Alchemy is a python abstraction that makes communication with databases easier. It is database agnostic, meaning that you use the same commands, regardless of whether you’re interacting with PostgreSQL, SQLite, MySQL, or some other relational database.
Set Up Today’s Exercises
- Create a new database by opening your terminal. From any directory, type:
psql -U postgresOnce you’re on the psql command prompt, create a new database called
orm_test:create database orm_test;Once you get a “Database Created” message, exit
psql(\q). -
Download the files:
Download today’s lecture files, unzip them, and save the
orm_introductionfolder in yourcsci344/lecturesdirectory.
ORM Sample Files -
Set Up Your Virtual Environment
Open VS Code. Then open the integrated VS Code terminal and navigate to your
orm-introductionfolder. From this directory, set up a virtual environment and install the dependencies as follows:poetry install -
Update your database connection string
Open the
.envfile and modify your connection string so that your postgresql password is reflected (versus 12345). Replace “12345” with whatever your postgres password is:DB_URL=postgresql+psycopg://postgres:12345@localhost/orm_test -
Populate your database
From the terminal, build your database as follows (from the command prompt from within the
orm-introductionfolder).poetry run python populate.py -
Run the SQLAlchemy Tester
poetry run python tester.py
What just happened?
In the intructions above, we created a new database, installed and configured our python files / libraries to interact with our database and populated our database. The
tester.pyscript that just ran contains a demo of different SQLAlchemy queries that you can do.This infrastructure will allow your users to query a database from the web browser.
What is an Object Relational Mapping (ORM)?
ORMs allow a programmer to associate user-defined Python classes with database tables, and instances of those classes (objects) with rows in their corresponding tables (more on ORM here). In other words, rather than writing SQL directly, you interact with SQL Alchemy “models” that issue SQL queries under-the-hood.
Post Model
class Post(db.Model):
# name of table I want to connect to:
__tablename__ = 'posts'
# reference to the columns with which I want the application
# to interact:
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
image_url = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False)
caption = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=True)
alt_text = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=True)
pub_date = db.Column(db.DateTime, nullable=False,
default=datetime.utcnow)
user_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('users.id', ondelete='cascade'),
nullable=False)
# read-only property for referencing User properties
user = db.relationship('User', backref="posts", lazy=False)
comments = db.relationship('Comment', cascade="all,delete-orphan", lazy='select',
order_by='Comment.pub_date', backref=db.backref('posts', lazy='joined'))
likes = db.relationship('LikePost', cascade="all,delete-orphan", lazy='select',
order_by='LikePost.timestamp', backref=db.backref('posts', lazy='joined'))
def __init__(self, image_url:str, user_id:int, caption:str=None, alt_text:str=None, pub_date:datetime=None):
self.image_url = image_url
self.user_id = user_id
self.caption = caption
self.alt_text = alt_text
self.pub_date = pub_date
Post Table
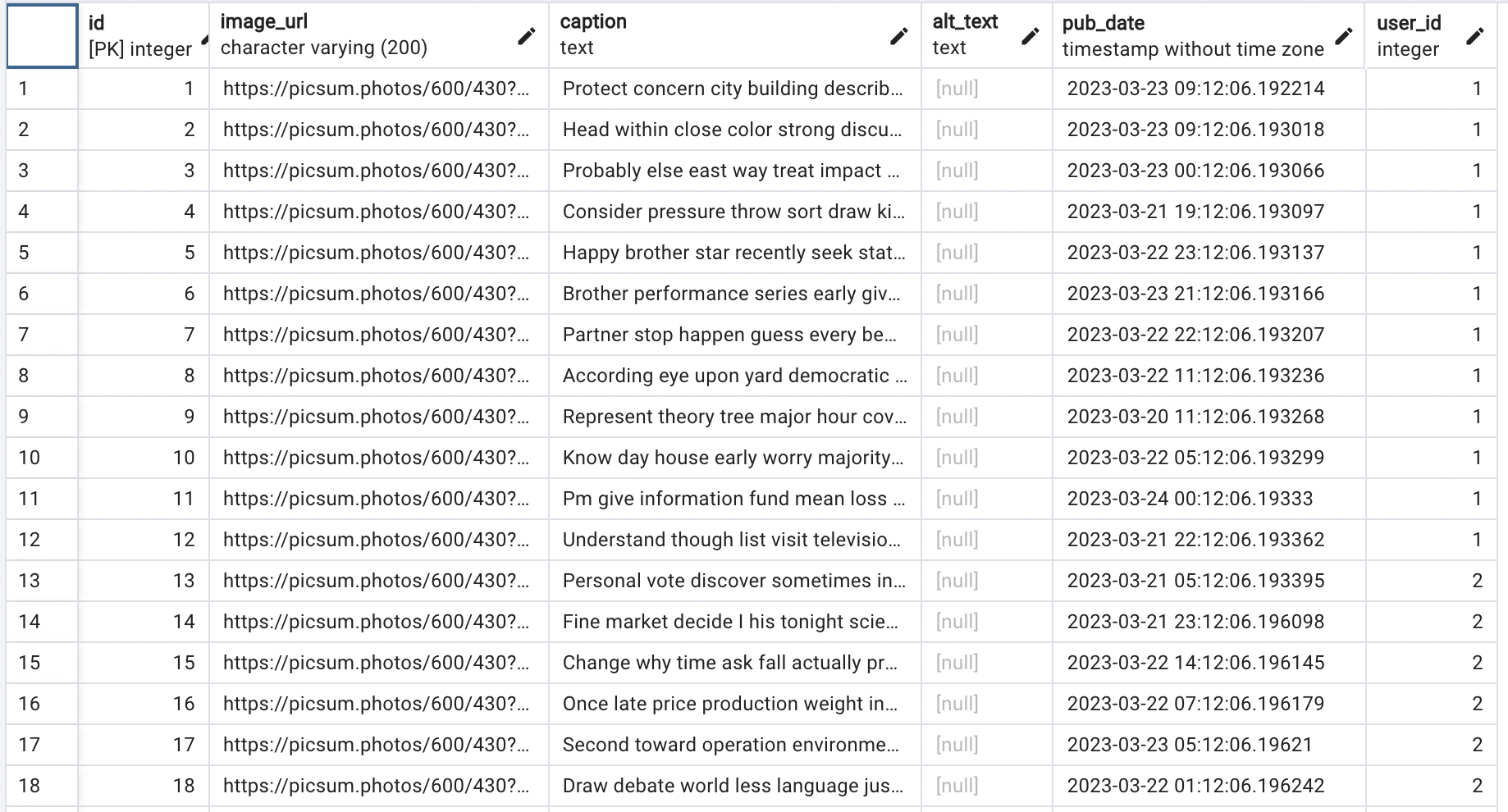
With this Post model definition, I am able to create, read, update, and delete records from the posts table. Some examples of how you would perform each of these operations are listed below:
Your Tasks
We will go through each of the functions in tester.py to try and understand what each one is doing. Please try to follow along carefully to make sure you understand the basic idea, as you will need to do this for HW5 & HW6.
Challenge Problems
SQLAlchemy Queries (tester.py)
- Create a function that creates a new fake user named “Walter” (make up their email, lastname, and username).
- Create a function that allows Walter to follow a new user (by creating a new
Followobject). - Create a function that allows Walter to like one of the posts of a user they’re following (by creating a new
LikePostobject). - Create a function that allows Walter to comment on a post of a user they’re following (by creating a new
Commentobject).
Flask Endpoints (app.py)
- Create a new endpoint that returns all of the
Postobjects that a user has liked. - Create an endpoint that allows a user to create a new
Commenton aPost.
To run the flask server, type:
poetry run flask run --debug